What Is Nanotechnology Applied to Paints?
Nanotechnology in paints involves the use of materials with structures smaller than 100 nanometers to enhance the physical, chemical, and mechanical properties of coatings. These nanoparticles modify the paint’s surface, achieving advanced effects such as self-cleaning, water repellence, scratch resistance, and antimicrobial protection.
Unlike traditional paints, those formulated with nanotechnology provide a more efficient interaction between particles and substrates, creating intelligent and functional surfaces that adapt to different environments and needs.
Brief History of Nanotechnology in Coatings
The concept of nanotechnology was introduced by Richard Feynman in 1959, but its application in paints did not develop until the late 1990s. Companies such as BASF, PPG Industries, and AkzoNobel began experimenting with titanium dioxide and silica nanoparticles to create more durable coatings.
Today, nanotechnology in paints is one of the most promising areas in the advanced materials sector, with an annual growth rate of over 20%, according to Global Market Insights (2025).
How Nanotechnology Paints Work
The fundamental principle is the manipulation of materials at the nanoscale to alter their properties in a controlled manner. Nanoparticles act as functional modifiers capable of improving adhesion, durability, gloss, and even endowing the surface with smart properties.
Molecular Structure and Behavior at the Nanoscale
Because nanoparticles are extremely small, they have a high surface-to-volume ratio, allowing for more efficient chemical reactions and homogeneous dispersion within the paint. This results in coatings that are more uniform, durable, and functional.
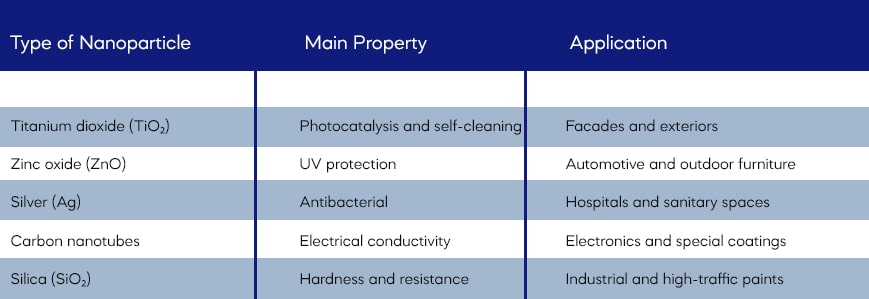
Main Benefits of Nanotechnology in Paints
Wear and Corrosion Resistance
Nanoparticles reinforce the coating structure, improving its resistance to scratches, friction, and oxidation. This extends the lifespan of painted surfaces, even in extreme environments.
Antibacterial and Self-Cleaning Properties
Thanks to the photocatalytic action of titanium dioxide, surfaces can degrade organic matter and eliminate bacteria with mere exposure to sunlight. This reduces maintenance costs and promotes healthier environments.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Nanotechnology paints can reflect solar radiation, maintaining more stable indoor temperatures and reducing energy consumption in buildings. Furthermore, many formulations use eco-friendly nanoparticles that minimize environmental impact.
Top 10
Top 10 Nanotechnology Paint Innovations
1-
Top 10 Nanotechnology Paint Innovations
- Self-Cleaning Paints with Titanium Dioxide (TiO₂)
Inspired by nature (the “lotus effect”), these paints repel water and dust, preventing dirt accumulation. - Antibacterial Coatings for Hospitals
Use silver nanoparticles that destroy bacterial membranes, reducing infections in medical areas. - Paints that Reduce Environmental Pollution
Through photocatalytic action, they capture nitrogen oxides from the air, helping to purify urban environments. - Paints with Enhanced UV Protection
ZnO and TiO₂ nanoparticles block ultraviolet rays, preventing color and material degradation. - Anti-Corrosion Coatings for Infrastructure
Nanoparticles create a protective barrier against moisture and chemicals—ideal for bridges and metal structures. - Electrically Conductive Paints
Perfect for electronics and electric vehicles, containing carbon nanotubes or graphene to enable charge dissipation. - Smart Thermal Coatings
Reflect or absorb heat depending on the ambient temperature, helping regulate building temperatures. - Silver Nanoparticle Paints
Used in hospitals, schools, and public transport for their long-lasting antimicrobial action. - Photocatalytic Paints for Healthy Interiors
Eliminate odors, fungi, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), improving indoor air quality. - Smart Coatings Responsive to the Environment
Can change color or reflectivity based on temperature or light variations—useful for signage or architectural design.
Industrial and Domestic Applications
In the Automotive Sector
Nanotechnology paints provide intense gloss, scratch resistance, and enhanced durability against UV rays.
In Construction and Architecture
Used for self-cleaning facades, antibacterial interiors, and thermal-insulating coatings.
In Electronics and Technology
Provide conductivity, moisture protection, and thermal stability in electronic components.
Current Challenges of Nanotechnology in Paints
Despite its advantages, the main challenges include high production costs, homogeneous nanoparticle dispersion, and evaluation of potential environmental risks. The lack of global regulations also limits widespread adoption.
Regulations and Safety in the Use of Nanoparticles
The European Union and organizations such as the OECD are developing legal frameworks to ensure controlled nanoparticle toxicity, protecting both end users and the environment. The use of biodegradable and traceable nanomaterials is being promoted.
The Future of Smart and Sustainable Paints
The future points toward self-sufficient, eco-friendly, and multifunctional coatings capable of repairing microcracks, absorbing pollutants, or generating solar energy. The convergence of artificial intelligence and nanotechnology will enable the design of paints with customized properties.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Are nanotechnology paints environmentally safe?
Yes, as long as stable and non-toxic nanoparticles are used. Most modern formulations are eco-friendly. - Can I apply nanotechnology paints at home?
Yes, there are commercial versions for both interiors and exteriors that offer UV protection and self-cleaning properties. - What’s the difference between regular and nanotechnology paints?
Nanotechnology paints offer greater durability, resistance, and functionality thanks to their nanoparticles. - Are nanotechnology paints expensive?
Initially, yes—but in the long run, they are more economical due to their low maintenance needs. - Do silver-based paints eliminate viruses as well as bacteria?
Some studies suggest yes, since silver can destroy viral envelopes, though it depends on the formulation.
Conclusion
Nanotechnology in paints represents a revolutionary shift toward smarter, more durable, and sustainable coatings. From self-cleaning facades to antibacterial surfaces, its application redefines protection and aesthetics. With ongoing advancements, nanotechnology paints not only beautify but also protect health, the environment, and the energy efficiency of spaces.

